Extracellular vesicles: unlocking therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine
۱۸ آذر ۱۴۰۳
115 بازدید
بدون دیدگاه

Introduction: Lithium (Li) is widely used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, but it may lead to toxicity in the reproductive system. Considering the harmful effect of Li consumption on fertility and the positive effect of magnesium sulfate (MgSo4) and moderate‑intensity training (MIT) on improving the quality of men’s sperm, the current research was conducted to determine the impact of MIT and MgSo4 on infertility caused by Li.
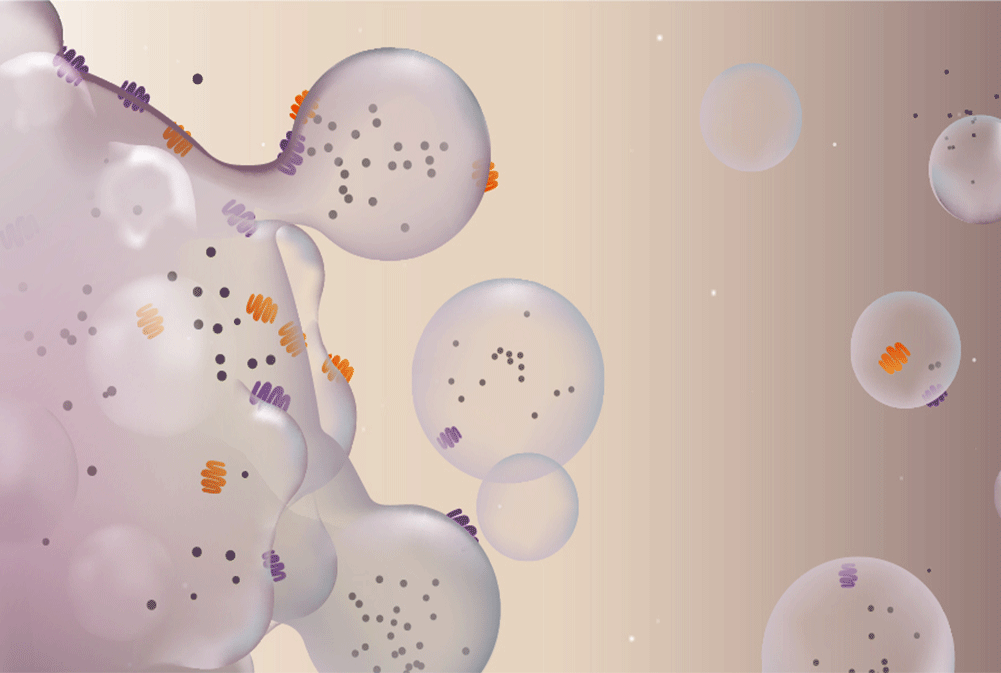
EVs can be broadly classified into two main subgroups based on their size and biogenesis: microvesicles (MVs) and exosomes. Microvesicles, ranging from 100 to 500 nm in diameter, are formed by budding off from the plasma membrane, representing a subgroup of larger vesicles. By contrast, exosomes are considerably smaller, with diameters of approximately30 to 150 nm, and are generated through the reverse budding of endosomal multivesicular bodies, released upon their fusion with the plasma membrane. Obtaining pure fractions of MVs and exosomes poses significant challenges due to difficulties in distinguishing them based on size, density, and overlapping protein markers. To address these complexities, there has been a proposal to standardize the terminology in line with the guidelines set forth by the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) in 2018. This effort aims to clarify methodological issues and accurately differentiate between MVs and exosomes. Furthermore, the ISEV established the term “EVs” in 2024 through the Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV) guidelines to encompass all particles released from cells.
The revitalizing impacts of EVs can be partially ascribed to the transmission of distinct protein and miRNA loads. An escalating fascination lies in pinpointing the subsets of EVs harboring optimal therapeutic capabilities. Recent research underscores that miRNAs are notably concentrated in the biologically potent exosome subset rather than the MV or shedding vesicle fraction. Consequently, this section delves into the significance of exosomes and other EVs in the context of tissue rejuvenation and the expansive field of regenerative medicine.
آدرس: اصفهان، اتوبان آقابابایی، خیابان سپهر، شهرک سلامت اصفهان، طبقه سوم
تلفن: 35548151-031 داخلی 602
شماره موبایل: 09024265006
ایمیل: pddrc.com@gmail.com